
Smart City
Concept of Smart City
There is a universally accepted definition of a smart city. This means different things to different people. The concept of Smart City, therefore, depends on the desire and improvement, the resources and aspirations of the inhabitants of the city, to change the level of evolving development, from the city to the city to the country for the country. Compared to Smart City Europe, say, India has a different meaning. Even in India, there is one way to define a smart city. Some technical boundaries are essential to guide cities in the mission. In the imagination of any city resident in India, the picture of a smart city is included in a wish list of infrastructure and services that describes its level of aspiration.
To provide for the needs of the aspirations and citizens, the purpose of developing the urban planners ideal is the entire urban ecosystem, which represents the four pillars of comprehensive development-institutional, physical, social and economic infrastructure. It can be a long-term goal and can work towards improving such comprehensive infrastructure in cities, adding on the layers of 'intelligences'. In the vision of the Smart City Mission, the aim is to promote cities to provide core infrastructure and to give a civilized quality of life to their citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of 'smart' solutions. The focus is on sustainable and inclusive development and the idea is to create compact areas to look for an exemplary model which will work as a light house for other interested cities. The mission of the Smart City Government is a bold, new initiative. It caters to the creation of similar smart cities in parts of different areas and in a smart city will be included elements of core core infrastructure, in order to set example, both can be repeated within and outside the smart city is:
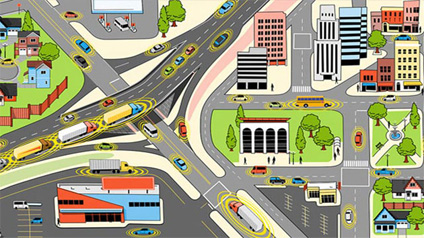
Enough water supply,
Assurance power supply,
Cleanliness, including clean waste management,
Efficient Urban Mobility and Public Transportation,
Affordable housing, especially for the poor,
Strong IT connectivity and digitization,
Good governance, especially e-governance and citizen involvement, sustainable environment,
Security and security of citizens, especially women, children and the elderly, and health and education.
This is not a comprehensive list, but more cities are free to add more applications.



